Saturday, August 26, 2006
Amock 0.9 beta
This is beta version of AOP based Mock.
Amock is AOP based Mock library. It currently support only 1.5version of JDK but it will soon support 1.4 version of JDK. And I hope to Implement Amock on C# and C++. For now, only java version is available. Source code will be available soon.
Pros
You can record even a static method call.
You can reduce your typing
Cons
Weaving time is slow
Aspectj can not handle Checked Exception. So, Needs manual works to throw checked exception on static method.
Prerequisite
JDK 1.5 version
Eclipse 3.2
AJDT 1.4.0
Download Amock libarary and documentation from
http://www.box.net/public/i3dxv1ba8g#main
and CGlib no dependency 2.1_3
http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/cglib/cglib-nodep-2.1_3.jar?download
To use this libary
First change project to AspectJ project.
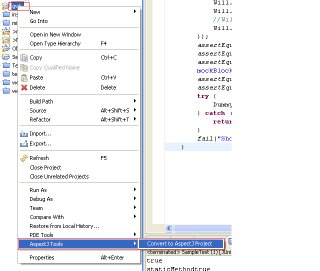
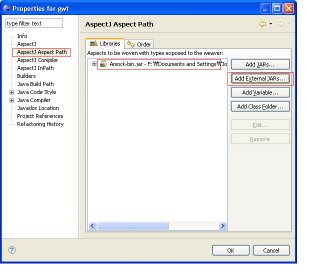
Second, Add 'Amock-bin.jar' in your AspectJ Aspect path.
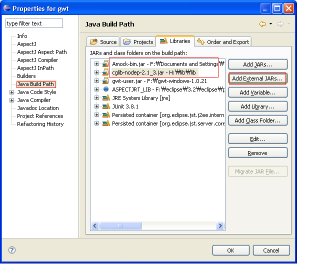
Third, Add 'Amock-bin.jar' and 'cglib-nodep-2.1_3.jar' in your Class path.
Now you ready to use Amock.
To throw Checked Exception on static method, Define ExceptionDefineAspect.aj on Aspectj Path
(package does not mater. Bold should be changed to exception you want to throw)
package my.amock.core;
import java.io.IOException;
public aspect ExceptionDefineAspect extends CommonAspect {
Object around() throws IOException : call(* *(..) throws IOException)
&& notInMockPackage()
&& if(isMockThrow(IOException.class, thisJoinPoint)) {
throw (IOException) getThrowable(thisJoinPoint);
}
}
Sample code: SimpleTest.java
package my.amock.example;
import my.amock.bracket.Mock;
import my.amock.bracket.Story;
import my.amock.util.A;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import static my.amock.util.Will.*;
class DivideAndDivide {
public int ADivideBDivideC(int a, int b, int c) {
DividerSingleton divider = DividerSingleton.getInstance();
int i = divider.divide(a, b);
return divider.divide(i, c);
}
}
class DividerSingleton {
private DividerSingleton() {
}
public static DividerSingleton getInstance() {
// Not yet implemented
return null;
}
public int divide(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException {
// Not yet implemented
return 0;
}
}
public class SimpleTest extends TestCase {
DividerSingleton divider;// mock
DivideAndDivide divideAndDivide;// test target
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
// create mock object
new Mock() {{
// private constructor need constructorExact()
divider = A.constructorExact(DividerSingleton.class).invoke();
// if it was public constructor
// divider = new DividerSingleton();
// if it was interface
// divider = A.mock(DividerSingleton.class);
}};
//create normal object
divideAndDivide = new DivideAndDivide();
}
public void testAdderSingleton() {
//recording scenario
new Story() {{
// One time call record for static method with return value
// Only static method need call() method;
//Will.call();
call(divider); DividerSingleton.getInstance();
//Will.ret();
ret(2); divider.divide(4, 2);
ret(1); divider.divide(2, 2);
}};
//test target object
int returnValue = divideAndDivide.ADivideBDivideC(4, 2, 2);
assertEquals(1, returnValue);
}
}
Sample code: SampleTest.javapackage my.amock.example;
import java.util.Comparator;
import my.amock.bracket.Story;
import my.amock.util.A;
import my.amock.util.Mock;
import my.amock.util.NotMock;
import my.amock.util.NotStory;
import my.amock.util.Will;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
class Dummy {
private int privateField = 1;
private int privateMethod() {
return privateField;
}
public static int staticMethod(String arg1, int arg2) {
return 2;
}
public Character aMethod(String arg1, Long arg2) {
return 't';
}
public int aMethodTwo(String arg1, int arg2) {
return 1;// privateMethod();
}
}
/**
* This class show how to use Amock (It is not an example of how to use a mock
* in unit test) In other word, it just show you functionality of Amock.
*
* @author Jonghyun Yoon
*
*/
public class SampleTest extends TestCase {
Comparator alwaysTrueComparator = new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return 0;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return super.equals(obj);
}
};
// It is a mock object because it is end with 'mock'
private Dummy dummyMock;
// It is not a mock object because @NotMock is attached
@NotMock
private Dummy notAMock;
// It is a mock object because @Mock is attached
@Mock
private Dummy mockDummy;
// It will be a mock object because mockBlock is instantiated in Mock block
private Dummy mockBlock;
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
// If an instance is created in the mock block then it will be a mock
// object.
new my.amock.bracket.Mock() {
{
mockBlock = new Dummy();
}
};
dummyMock = new Dummy();
notAMock = new Dummy();
mockDummy = new Dummy();
}
public void testBockStory() {
// In Story block, All mock method calling will be recorded.
new Story() {
{
dummyMock.aMethod("test", 1L);
// Can use static import like
// ret('x'); mockDummy.aMethod("test", 2L);
Will.ret('x');
mockDummy.aMethod("test", 2L);
// Can specify comparator.
Will.with(null, alwaysTrueComparator);
mockBlock.aMethod("test", 2L);
// Will.call() can use to record static method.
Will.call();
Dummy.staticMethod("test", 1);
}
};
assertEquals(Character.valueOf(Character.MIN_VALUE), dummyMock.aMethod(
"test", 1L));
assertEquals(1, notAMock.aMethodTwo(null, 0));
assertEquals(Character.valueOf('x'), mockDummy.aMethod("test", 2L));
mockBlock.aMethod("test", 0L);
assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), (Integer) A.field(notAMock,
"privateField").get());
assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), (Integer) A.methodExact(notAMock,
"privateMethod").invoke());
try {
Dummy.staticMethod("test", 2);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return;
}
fail("Should not reach here");
}
// Method end with 'Story' will become Story block.
public void aStory() {
// System.out.println("Story enter");
dummyMock.aMethod("test", 1L);
}
// This is Story block because @Story is attached.
@my.amock.util.Story
public void storyTwo() {
// Can use static import
Will.ret('x');
mockDummy.aMethod("test", 2L);
}
// This is not Story block because @NotStory is attached.
@NotStory
public void notAStory() {
try {
// There is no recorded action, So it will throw Exception.
mockBlock.aMethod("test", 2L);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return;
}
fail("Should not reach here");
}
public void testStoryMethodStoryEnd() {
aStory();
storyTwo();
notAStory();
// One Time Record
Will.call(1);
Dummy.staticMethod("test", 1);
assertEquals(Character.valueOf(Character.MIN_VALUE), dummyMock.aMethod(
"test", 1L));
assertEquals(1, notAMock.aMethodTwo(null, 0));
assertEquals(Character.valueOf('x'), mockDummy.aMethod("test", 2L));
assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), (Integer) A.field(notAMock,
"privateField").get());
assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), (Integer) A.methodExact(notAMock,
"privateMethod").invoke());
assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), (Integer) Dummy
.staticMethod("test", 1));
}
}